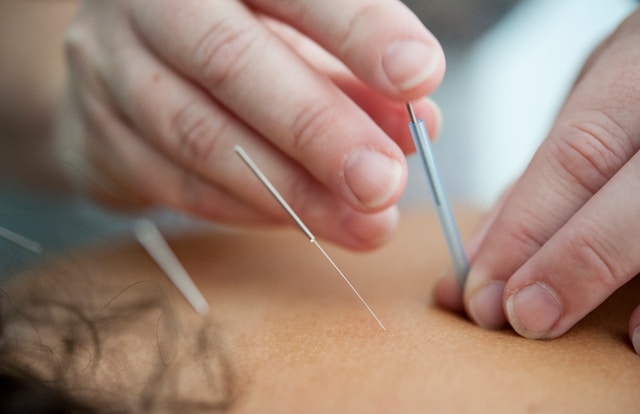
Acupuncture, an ancient practice rooted in traditional Chinese medicine, has stood the test of time as a therapeutic modality. This technique involves the insertion of fine needles into specific points on the body, known as acupuncture points, to restore balance and promote natural healing. The purpose of this article is to shed light on the scientific underpinnings of the practice’s healing effects, providing a comprehensive understanding for both practitioners and patients.
The Basics of Acupuncture
Acupuncture is based on the concept of qi (pronounced “chee”), which is considered the vital life force that flows through pathways called meridians. According to traditional Chinese medicine, imbalances or blockages in the flow of qi can lead to health issues. The practice aims to restore this balance by stimulating specific points along the meridians.
During an acupuncture session, the practitioner carefully selects and inserts sterile needles into these points. The needles are typically made of stainless steel and are so fine that their insertion is often barely felt. Once in place, the needles may be gently manipulated to enhance their therapeutic effect, which can include twisting or applying heat.
Acupuncture Techniques
In addition to traditional needle acupuncture, several other techniques are used to stimulate acupuncture points:
- Moxibustion: This involves burning a small, cone-shaped amount of moxa (dried mugwort) on or near the skin at an acupuncture point. The heat from the moxa is believed to penetrate deeply into the body, enhancing the therapeutic effects of the treatment.
- Cupping: Glass or plastic cups are applied to the skin, creating a vacuum that gently pulls the skin upward. This is thought to promote blood flow and relieve muscle tension.
- Electroacupuncture: A mild electric current is passed between two acupuncture needles, providing a continuous stimulus to the acupuncture points.
- Acupressure: Instead of needles, manual pressure is applied to acupuncture points, making it a non-invasive option for those who are needle-sensitive.
Each of these techniques offers a unique approach to stimulating acupuncture points, and practitioners may choose one or a combination of techniques based on the patient’s needs and preferences.
Biological Mechanisms of Acupuncture
The healing effects of acupuncture are believed to stem from its ability to trigger various physiological responses. One of the primary mechanisms is the increase in blood flow to the areas surrounding the acupuncture points. This enhanced circulation can help reduce inflammation, promote tissue repair, and alleviate pain.
Furthermore, the practice is known to stimulate the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural pain-relieving chemicals. This can lead to a reduction in pain and a feeling of relaxation and well-being. Additionally, the practice has been shown to activate the nervous system, sending signals to the brain that can modulate bodily functions and improve overall health.
Acupuncture and Pain Relief
Pain relief is one of the most well-documented benefits of acupuncture. It is particularly effective for chronic pain conditions such as osteoarthritis, lower back pain, and migraines. The practice is believed to work for pain relief by altering the brain’s pain processing pathways, reducing the intensity of pain signals and promoting a sense of relaxation.
Acupuncture’s Impact on the Nervous System
The effects of acupuncture on the nervous system are multifaceted. It has been shown to influence the central nervous system, which can lead to changes in the production and release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine. These neurotransmitters play a crucial role in mood regulation and stress response. Additionally, the practice can enhance the signaling of nerves, leading to improved communication between the brain and various parts of the body.
Acupuncture and the Immune System
Recent studies suggest that the practice can have a positive impact on the immune system. By stimulating certain acupuncture points, it can reduce inflammation and increase the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting off infections and diseases. This aspect of acupuncture is particularly promising for individuals looking to boost their immune health and resilience.
Acupuncture has been a subject of interest in the medical community for its potential therapeutic benefits. Numerous research studies have been conducted to evaluate its efficacy in various health conditions. Here, we will explore some of the key findings from these studies.
The Clinical Evidence Supporting Acupuncture
- Chronic Pain Relief: One of the most well-documented benefits of acupuncture is its ability to relieve chronic pain. A meta-analysis published in the Archives of Internal Medicine analyzed data from 29 studies involving nearly 18,000 patients. The researchers found that acupuncture was effective in relieving chronic pain, including back and neck pain, osteoarthritis, and chronic headaches, with effects persisting over time (Vickers et al., 2012).
- Migraine Prevention: Acupuncture has also been studied as a preventive treatment for migraines. A systematic review and meta-analysis published in The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews evaluated 22 trials with 4,985 participants. The review concluded that acupuncture reduces the frequency of migraine attacks and may be at least similarly effective as treatment with prophylactic drugs (Linde et al., 2016).
- Improvement in Cancer-related Symptoms: Acupuncture has been explored as a complementary therapy for managing symptoms associated with cancer and its treatment. A randomized controlled trial published in JAMA Oncology investigated the efficacy of acupuncture in reducing symptoms of aromatase inhibitor-related joint pain in breast cancer patients. The study found that acupuncture significantly reduced joint pain scores compared to sham acupuncture and usual care (Hershman et al., 2018).
- Alleviation of Depression: The potential of acupuncture in treating depression has been explored in several studies. A meta-analysis published in PLOS ONE reviewed 29 randomized controlled trials involving 2,283 patients with depression. The analysis indicated that acupuncture, either alone or in combination with medication, showed significant improvements in depressive symptoms compared to medication alone or sham acupuncture (Zhang et al., 2018).
- Management of Insomnia: Acupuncture has been proposed as a treatment for insomnia. A systematic review and meta-analysis published in Sleep Medicine Reviews examined 46 randomized controlled trials involving 3,811 participants. The review concluded that the practice was more effective than no treatment and at least as effective as, or possibly more effective than, medication in improving sleep quality (Cao et al., 2019).
Safety and Side Effects
Acupuncture is generally considered safe when performed by a trained and qualified practitioner. Common side effects are minimal and may include slight bruising or bleeding at the needle sites. In rare cases, more serious complications can occur, such as infections or organ injury, emphasizing the importance of seeking treatment from a licensed acupuncturist.
Finding the Right Acupuncturist
Selecting the right healthcare professionals is crucial for receiving effective and personalized treatment. At our clinic, we take pride in our team of licensed acupuncturists, each skilled in providing tailored acupuncture treatments designed to meet your unique health needs. Our acupuncturists bring a wealth of experience in traditional and modern acupuncture techniques to optimize your wellness benefits.
We invite you to visit our Team Page to learn more about the qualifications and specializations of our dedicated professionals. When you’re ready to take the first step toward enhanced wellness, scheduling a consultation is straightforward through our Booking Page. Here, you can find a time that seamlessly fits into your schedule.
Conclusion
Acupuncture represents a fascinating intersection between ancient wisdom and modern science. Its ability to promote healing through the stimulation of physiological responses is supported by a growing body of evidence. As our understanding of the practice’s mechanisms continues to evolve, its integration into contemporary healthcare practices is likely to expand, offering a holistic and effective approach to health and well-being.
References:
- Vickers, A. J., et al. (2012). Acupuncture for Chronic Pain: Individual Patient Data Meta-analysis. Archives of Internal Medicine, 172(19), 1444–1453.
- Linde, K., et al. (2016). Acupuncture for the prevention of episodic migraine. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 6, CD001218.
- Hershman, D. L., et al. (2018). Effect of Acupuncture vs Sham Acupuncture or Waitlist Control on Joint Pain Related to Aromatase Inhibitors Among Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncology, 4(7), 1144–1152.
- Zhang, Z. J., et al. (2018). The effectiveness and safety of acupuncture therapy in depressive disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLOS ONE, 13(7), e0202288.
- Cao, H., et al. (2019). Acupuncture for Treatment of Insomnia: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 47, 62–73.